Cannabis has an incredibly broad medicinal effect. This is due to the many active substances in the plant, each of which has its own specific properties. These substances can be divided into different groups including terpenes, flavonoids and cannabinoids. The latter group consists of more than 100 substances that are similar to substances that our own body also produces.
When our bodies produce them we call them endo- and when they come out of the plant they are phytocannabinoids. These chemicals fit perfectly on receptors that belong to our endocannabinoid system (ECS). A system that plays a role in nerves, stress and restless feelings. It also functions as a natural tranquillizer for a good sleep and a healthy night’s sleep, it plays a role in the formation of the state of mind and the functioning of the nervous system. It also contributes to blood sugar metabolism, plays a role in the skin’s ability to recover, in bone formation (helps bone growth), blood pressure, oxygen transport, stomach function, attenuates mood swings during the menstrual cycle and protects against signs of old age. The endocannabinoid system is important for the normal functioning of the body. It is actually millions of years old from an evolutionary point of view. It has also been found in mammals, fish, urchins and molluscs.
We look at the five most important phytocannabinoids and their medicinal applications.
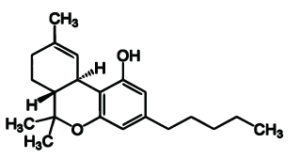
– Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
The best known (and most notorious) substance in weed is undoubtedly THC. It is also the most common cannabinoid in cannabis. From THC you can get stoned. For opponents of cannabis, the euphoria you get from the plant is reason enough to demonise the plant. Yet THC is anything but bad.
To start with, it stimulates the appetite, better known as the ‘eating kick’. And that is very pleasant for, for example, cancer patients who, thanks to chemotherapy, eat badly or have no appetite for it. THCV is a cannabinoid that is very similar to THC and triggers the same receptors, but reduces the appetite. That is why this substance is good to use for people who are addicted to food or have obesity-related health problems. Think for example of type 2 diabetes.
In addition, more and more is known about the possible tumour inhibiting effect of the substance. Many patients have already successfully treated their tumours with THC weed oil. It also helps against diseases such as: HIV/AIDS, Chronic pain, Multiple sclerosis (MS), Glaucoma, Fibromyalgia, Huntingtons, ALS, Gilles de la Tourette, Sleep apnea.
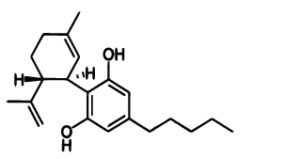
– Cannabidiol (CBD)
After THC, cannabidiol is definitely the most popular cannabinoid. In the Netherlands there is also almost no drugstore or nature shop where CBD oil is not on the counter. The reason that this substance has become so popular in a short period of time is that it is not psychoactive, but still has a calming effect on the central nervous system. Because of this, the substance is also used more for children than its psychoactive cannabinoid colleague.
CBD has been proven effective in various forms of epilepsy, MS, chronic pain, cancer, anxiety, depression, diabetes, arthritis, Crohn’s disease and various inflammations.
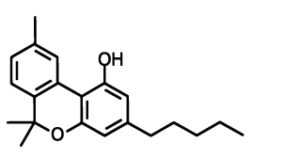
– Cannabinol (CBN)
If cannabis is exposed to too much air or heat, THC oxidizes and becomes CBN. In itself, CBN is slightly psychoactive. But if you combine it with THC, it becomes heavier and produces the well-known ‘couch-lock’ effect. A state of ultimate relaxation (and fatigue) in which simple tasks such as getting off of the couch become major obstacles. Although it can be annoying if you still have things to do, the effect is ideal if you have trouble sleeping. CBN also counteracts nausea and epileptic seizures.
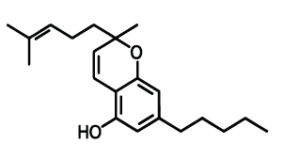
– Cannabigerol (CBG)
CBG is actually a building block for the cannabinoids THC and CBD, it is their precursor. The substance itself is more common in industrial hemp than in weed. Because in industrial hemp it is not converted to THC and only partly to CBD. Nowadays, seed makers also select this substance for its antibacterial and anti-tumour properties. Cannabigerol also helps lower eye pressure in glaucoma patients, reduce nausea, reduce anxiety and treat gastrointestinal problems such as irritable bowel syndrome.
– Cannabichromene (CBC)
In many types of weed, CBC is the most common cannabinoid – next to THC. It is not psychoactive but helps to relieve pain, inhibit tumor growth and stimulate bone and brain cell growth. CBC also improves your mood and has antibacterial and anti-fungal properties.
As mentioned before, there are more than 100 cannabinoids in the plant, and this is only the tip of the iceberg.


